Better farming for a changing climate
Still, growing one’s own food in this environment is not easy. The climate has generally gotten hotter and drier, with dry spells punctuated by intense storms and winds, and unpredictable rains. Scorching heat evaporates water quickly and can easily whither young seedlings.
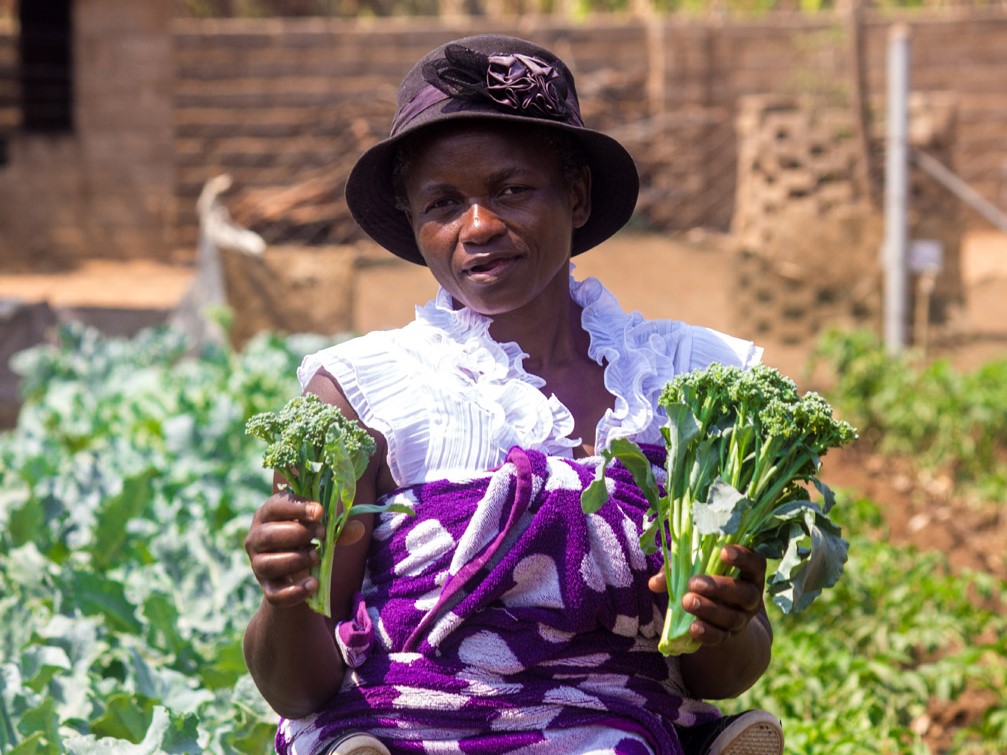
“At this clinic garden, we were taught smart agriculture techniques as a way of combating the effects that climate change was having on our harvest,” says Beauty Manyazda, another new mother who works regularly at the Chibuwe Clinic garden. “We learnt techniques such as conservation farming and mulching.”
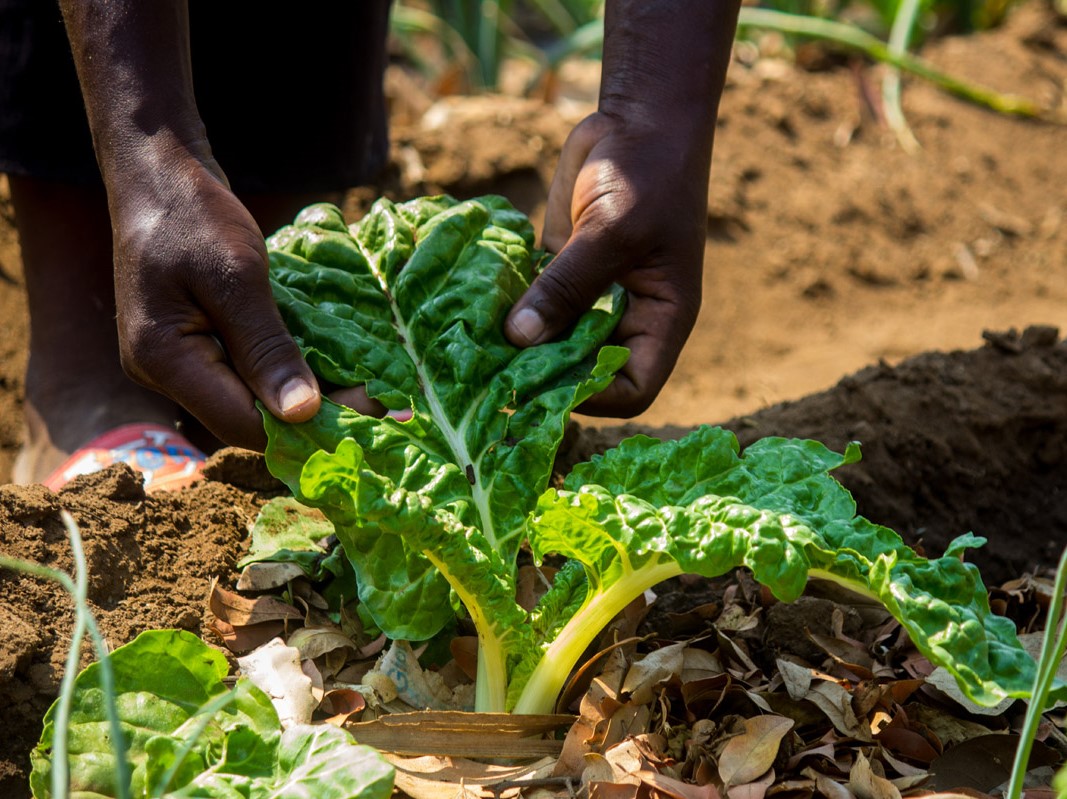
Conservation farming is an approach that aims to improve soil moisture and health by minimising the intensive tilling and plowing associated with large-scale crop production. Mulching is one very common conservation technique in which straw, leaves or other organic matter is laid down on the soil between the crops. This keeps moisture from evaporating, while discouraging weeds and providing nutrients to the soil as the mulch decays.
Such techniques are increasingly critical as climate change makes farming more difficult. “Our rainfall patterns have changed over the years,” explains Lucky. “We used to get rain in October, when we would sow the seeds for our crops. Now, we get rains in January. So the seeds we put in the ground get damaged waiting for the rainfall.”
Meanwhile, storms, droughts and heatwaves have become more and more intense, says Lucky. “Temperatures have continued to rise and this has resulted in regular, violent winds,” she notes. “These winds have destroyed our homes. We also get floods which also contribute to the destruction.”
Amid these challenges, the garden provides also provides other nourishing ingredients: the joy and satisfaction of being able to work and provide sustenance while also being among plants, close the soil with other women at her side.
“I love gardening,” says Lucky, her baby tied to her back, fast asleep as she picks a handful of chard. “The green nature of the garden warms my heart. With the garden, I know my family will always have a home-grown, nutritious meal.”
 Red Cross Red Crescent magazine
Red Cross Red Crescent magazine 










 Tech & Innovation
Tech & Innovation Climate Change
Climate Change Volunteers
Volunteers Migration
Migration